NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Atoms in PDF form free download. Solutions of Chemistry, Bio, Maths and other subjects are also given on NCERT Solutions page. Additional questions based on topic Atoms are given below for practice.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 12

Go back to NCERT Solutions 12 Physics Main Page
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 12 Atoms in PDF form with the links given below.
- Study Online Exercises & Additional Solutions
- Download Exercises Solutions
- Download Additional Exercises Solutions
- Numerical Questions for practice (Select the Topic)
- NCERT Book chapter 12
- Revision Book Chapter 12
Questions based on Atoms for practice
Numerical problems and conceptual questions based on 12 Physics chapter 12 Atom are given below. These questions provides a perfect practice for not only CBSE board exams but also entrance exams. So, after going through the NCERT Chapter, students should do these as a practice questions.
Rutherford’s Atomic Model
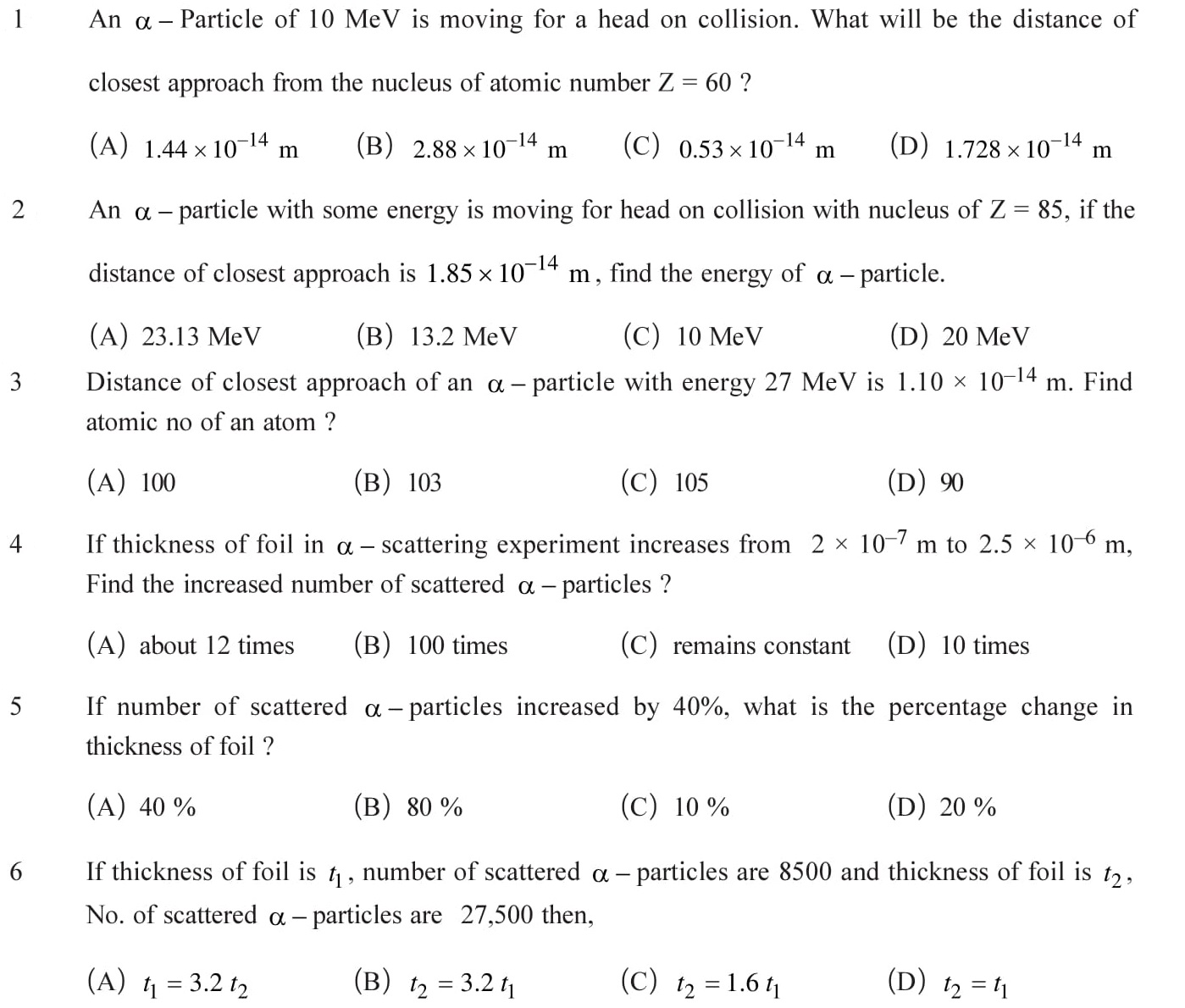
Scattering of alpha particle due to gold foil, impact parameter and relation with angle of deviation. Repulsive force between alpha particle and nucleus, the concept of closest approach. According to Rutherford, orbit of an electron is not circular but spiral and motion of an electron ends inside the nucleus. In this case the atom cannot remain stable. See Answers.
Bohr’s Atomic Model
Bohr’s atomic model and energy levels of Hydrogen atom. Bohr’s postulates for the revolutions of electrons. Kinetic and potential energy of an revolving electron. Limitations of Bohr’s model: The orbits of an electron need not to be circular.There is an odd combination of classical and quantum mechanics. Unable to explain the relative intensities of the spectral lines. Fine structure of spectral lines can not be explained. Unable to explain the arrangement of electrons in atoms. See Answers.



Hydrogen Spectrum
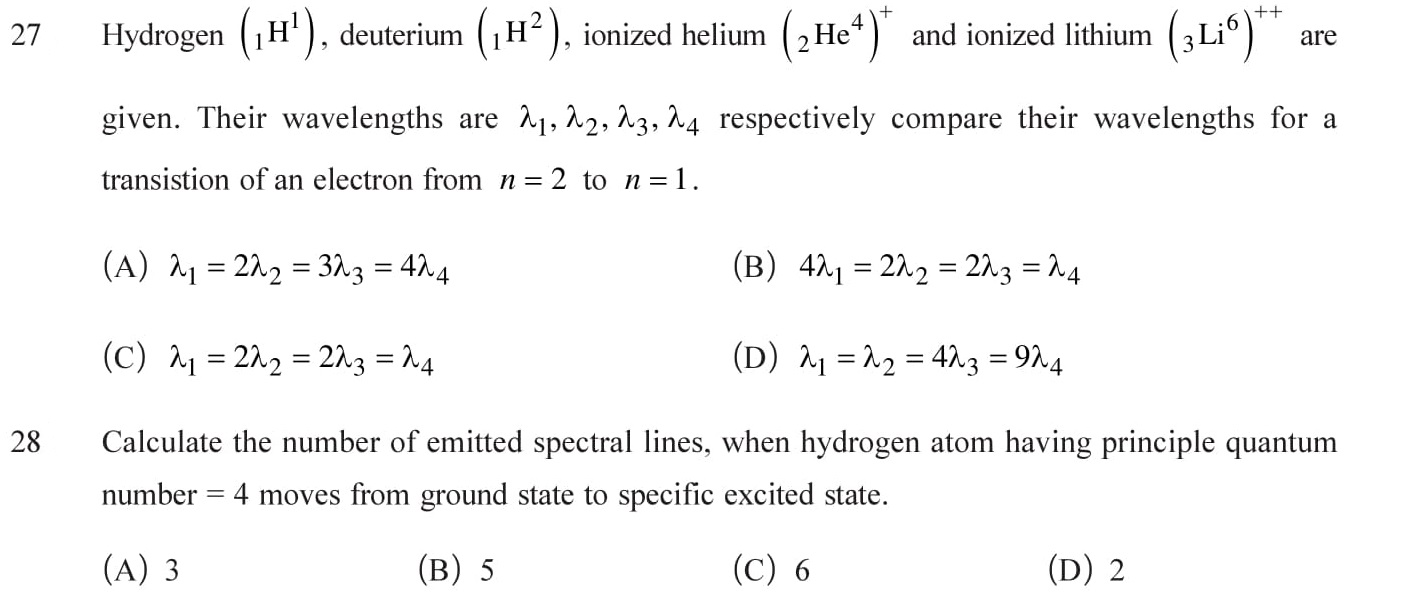
Hydrogen spectrum (When Hydrogen electrically discharged at low pressure, atom excited and emits radiation of certain wavelengths. The group of these radiations is called Hydrogen spectrum.), Lyman, Balmar, Paschen, Brackett and Pfund series. See Answers.

Excitation and Ionization energy
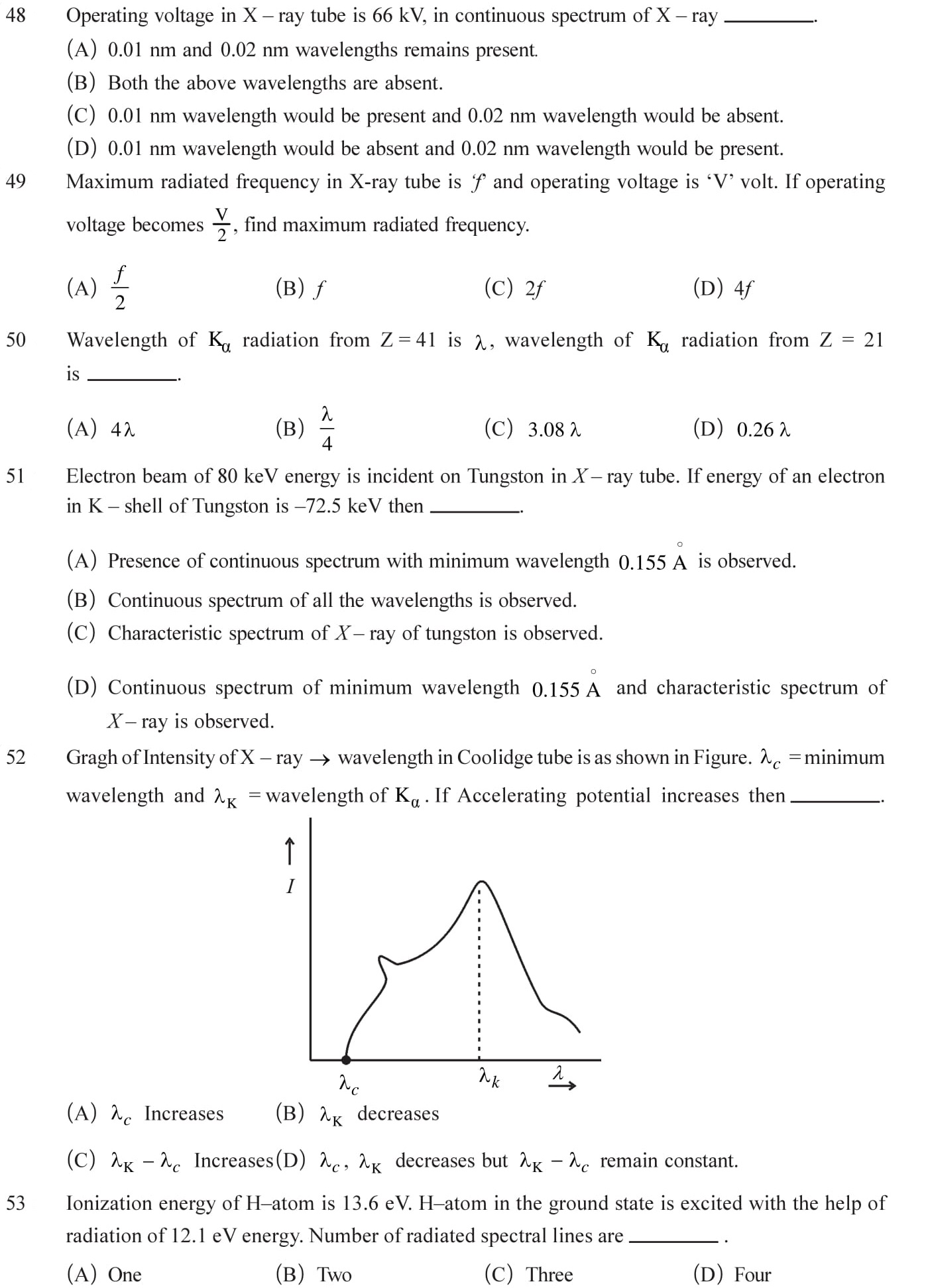
Excitation and Ionization energy and potential of an electron. Emission and absorption spectrum and relative intensity. See Answers.


Answers
1 (D), 2 (B), 3 (B), 4 (A), 5 (A), 6 (B), 7 (C), 8 (B), 9 (A), 10 (C), 11 (C), 12 (B), 13 (B), 14 (D), 15 (B), 16 (C), 17 (D), 18 (D), 19 (C), 20 (B), 21 (C), 22 (C), 23 (B), 24 (C), 25 (A), 26 (D), 27 (D), 28 (C), 29 (C), 30 (D), 31 (A), 32 (A), 33 (A), 34 (A), 35 (A), 36 (C), 37 (D), 38 (A), 39 (C), 40 (B), 41 (C), 42 (B), 43 (C), 44 (A), 45 (C), 46 (D), 47 (C), 48 (D), 49 (A), 50 (A), 51 (D), 52 (C), 53 (C), 54 (B), 55 (B).
Go back to top
Or Select your topic:
- Rutherford’s Atomic Model
- Bohr’s Atomic Model
- Hydrogen Spectrum
- Excitation and Ionization energy
- Previous Chapter: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- Next Chapter: Nuclei
- Main Page: NCERT Solutions 12 Physics