NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei Chapter end exercises and additional exercises in PDF form. Sols of other subjects please Click Here. Questions based on numerical are generally asked from this chapter in CBSE Exams. That is why, some numerical with answers are given below for practice.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13

Go back to NCERT Solutions 12 Physics Main Page
Download NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 13 Nuclei in PDF format with the links given below.
- Study Online Exercises & Additional Exercises
- Download Exercises Solutions
- Download Additional Exercises Solutions
- Extra Questions for Practice (Select your Topic)
- NCERT Book chapter 13
- Revision Book Chapter 13
Practice Questions with Numerical Problems on Nuclei
Following questions are providing a good practice on Nuclei chapter. It includes the questions, frequently asked in CBSE exams, JEE mains or NEET exams. It is a medium of good practice of this chapter. Question number 56 to 118 are given below. To see the question number 1 to 55, please Click Here.
Constitution of Nucleus
Atomic mass and the components of nucleus – proton and neutron. Atomic mass, relation of atomic mass, mass of neutron and mass of protons. Mass defect and numerical based on mass defect. Concepts of Isobars, Isotopes, Isotones (The nuclei for which the neutron number (N = A – Z) is same are called isotones.) and Isomers. Electrostatic and nuclear forces and relations of binding energy with mass defect. See Answers.



Radioactivity
Natural phenomena of radioactivity, law of radio active decay, Becquerel as a unit of rate of radioactivity. Alpha, beta and gamma decay and constitution of daughter nuclei. Nuclear reactors – Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion. When two proper light nuclei are fused at a very high temperature to form a heavy nucleus,
enormous energy is produced, such process is called thermonuclear fusion. See Answers.


Activity: Radioactive Constant
If N is the original quantity of any radioactive substance, then dN/dt is called the rate of disintegration or the decay rate or activity (I) of that element at time t. Activity means the number of nuclei decaying per unit time. 1 disintegration oceur in one second, then activity of body is called 1 Becquerel. 1 Bq = 1 disintegration / sec. Half life and mean life of a radioactive substance and the relation between them. See Answers.


Answers
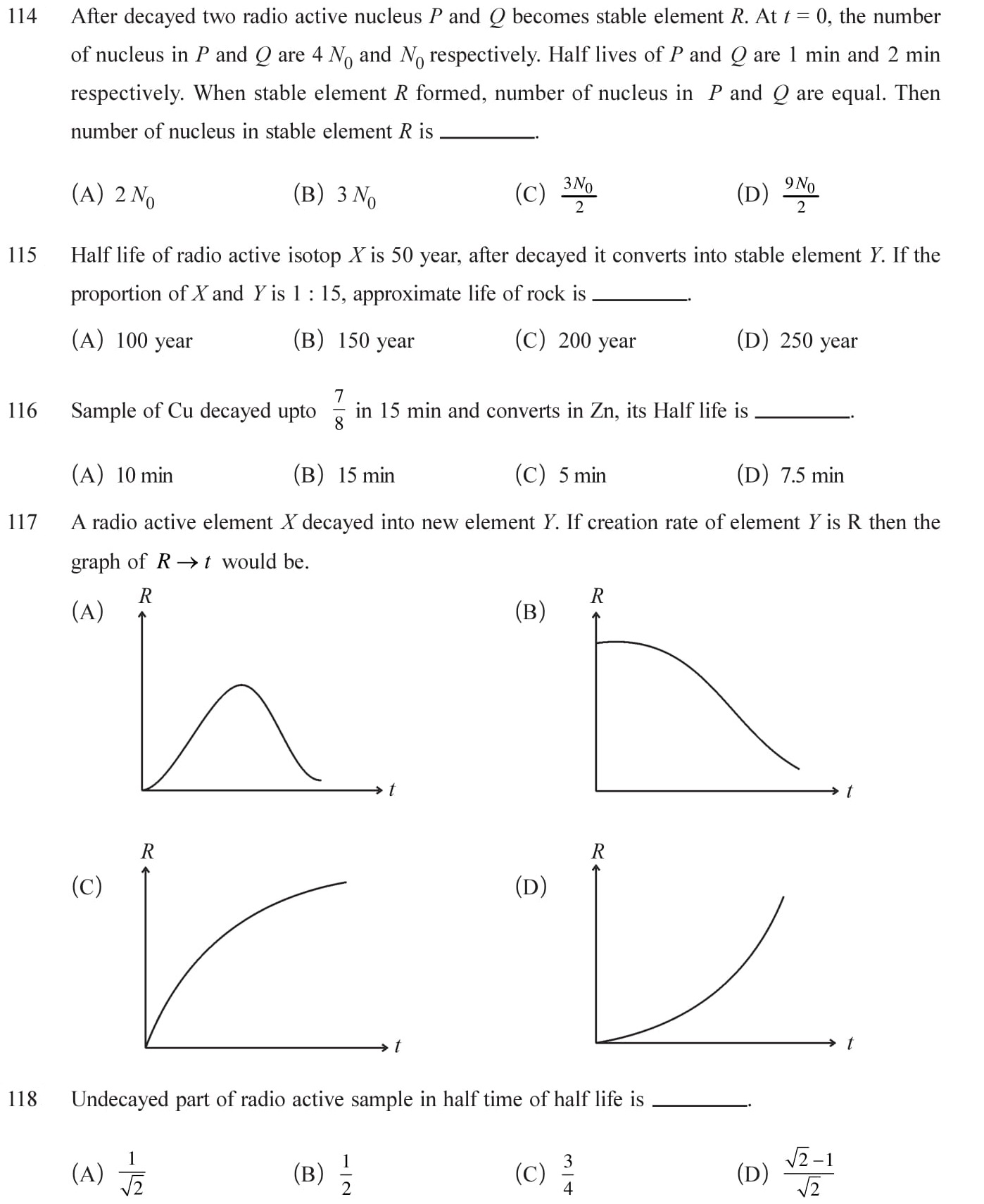
56 (C), 57 (C), 58 (B), 59 (D), 60 (B), 61 (B), 62 (C), 63 (D), 64 (C), 65 (C), 66 (D), 67 (A), 68 (D), 69 (A), 70 (D), 71 (C), 72 (D), 73 (A), 74 (C), 75 (B), 76 (C), 77 (A), 78 (B), 79 (A), 80 (C), 81 (A), 82 (B), 83 (B), 84 (C), 85 (C), 86 (B), 87 (A), 88 (A), 89 (C), 90 (B), 91 (A), 92 (C), 93 (C), 94 (A), 95 (A), 96 (C), 97 (C), 98 (D), 99 (D), 100 (A), 101 (B), 102 (C), 103 (D), 104 (D), 105 (D), 106 (D), 107 (A), 108 (D), 109 (B), 110 (C), 111 (C), 112 (A), 113 (C), 114 (D), 115 (C), 116 (C), 117 (C), 118 (A).
Go back to top
Or Select your topic:
- Constitution of Nucleus
- Radioactivity
- Activity: Radioactive Constant
- Previous Chapter: Atoms
- Next Chapter: Semiconductor Electronics
- Main Page: NCERT Solutions 12 Physics